알고리즘/자료구조
C언어 단순 연결 리스트
sshhhh
2023. 8. 24. 17:02
Source Code1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// 단순 연결 리스트의 노드 구조를 구조체로 정의
typedef struct ListNode
{
char data[4];
struct ListNode* link;
} listNode;
// 리스트의 시작을 나타내는 head 노드를 구조체로 정의
typedef struct
{
listNode* head;
} linkedList_h;
// 공백 연결 리스트를 생성하는 연산
linkedList_h* createLinkedList_h(void)
{
linkedList_h* L;
L = (linkedList_h*)malloc(sizeof(linkedList_h));
L->head = NULL; // 공백 리스트이므로 NULL로 설정
return L;
}
// 연결 리스트의 전체 메모리를 해제하는 연산
void freeLinkedList_h(linkedList_h* L)
{
listNode* p;
while (L->head != NULL) {
p = L->head;
L->head = L->head->link;
free(p);
p = NULL;
}
}
// 연결 리스트를 순서대로 출력하는 연산
void printList(linkedList_h* L)
{
listNode* p;
printf("L = (");
p = L->head;
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("%s", p->data);
p = p->link;
if (p != NULL) printf(", ");
}
printf(") \n");
}
listNode* createNode(char* x)
{
listNode* newNode;
newNode = (listNode*)malloc(sizeof(listNode)); // 삽입할 새 노드 할당
strcpy(newNode->data, x); // 새 노드의 데이터 필드에 x 저장
newNode->link = NULL;
return newNode; //주소를 반환
}
// 첫 번째 노드로 삽입하는 연산
void insertFirstNode(linkedList_h* L, char* x)
{
listNode* newNode;
newNode = createNode(x);
newNode->link = L->head;
L->head = newNode;
}
// 노드를 pre 뒤에 삽입하는 연산
void insertMiddleNode(linkedList_h* L, listNode* pre, char* x)
{
listNode* newNode;
newNode = createNode(x);
if (L == NULL)
{ // 공백 리스트인 경우
newNode->link = NULL; // 새 노드를 첫 번째이자 마지막 노드로 연결
L->head = newNode;
}
else if (pre == NULL)
{ // 삽입 위치를 지정하는 포인터 pre가 NULL인 경우
L->head = newNode; // 새 노드를 첫 번째 노드로 삽입
}
else
{
newNode->link = pre->link; // 포인터 pre의 노드 뒤에 새 노드 연결
pre->link = newNode;
}
}
// 마지막 노드로 삽입하는 연산
void insertLastNode(linkedList_h* L, char* x)
{
listNode* newNode;
listNode* p;
newNode = createNode(x);
if (L->head == NULL)
{ // 현재 리스트가 공백인 경우
L->head = newNode; // 새 노드를 리스트의 시작 노드로 연결
return;
}
// 현재 리스트가 공백이 아닌 경우
p = L->head;
while (p->link != NULL)
p = p->link; // 현재 리스트의 마지막 노드를 찾음
p->link = newNode; // 새 노드를 마지막 노드(temp)의 다음 노드로 연결
}
int main()
{
linkedList_h* L;
L = createLinkedList_h();
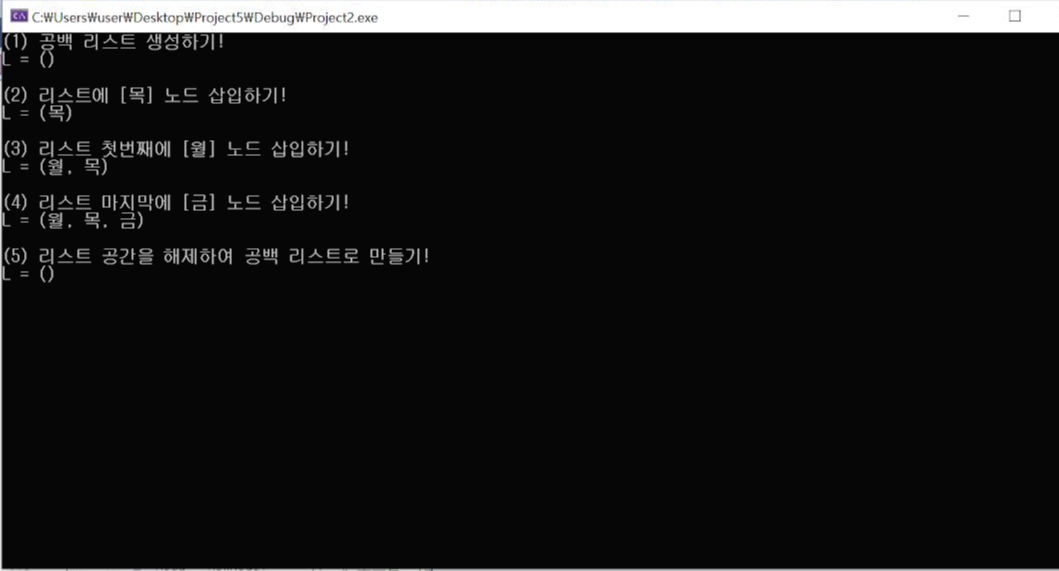
printf("(1) 공백 리스트 생성하기! \n");
printList(L); getchar();
printf("(2) 리스트에 [수] 노드 삽입하기! \n");
insertFirstNode(L, "수");
printList(L); getchar();
printf("(3) 리스트 마지막에 [금] 노드 삽입하기! \n");
insertLastNode(L, "금");
printList(L); getchar();
printf("(4) 리스트 첫 번째에 [월] 노드 삽입하기! \n");
insertFirstNode(L, "월");
printList(L); getchar();
printf("(5) 리스트 공간을 해제하여 공백 리스트로 만들기! \n");
freeLinkedList_h(L);
printList(L);
getchar();
return 0;
}
실행 결과1
Source Code2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct ListNode
{
char data[4];
struct ListNode* link;
} listNode;
typedef struct
{
listNode* head;
} linkedList_h;
linkedList_h* createLinkedList_h(void)
{
linkedList_h* L;
L = (linkedList_h*)malloc(sizeof(linkedList_h));
L->head = NULL;
return L;
}
void freeLinkedList_h(linkedList_h* L)
{
listNode* p;
while (L->head != NULL)
{
p = L->head;
L->head = L->head->link;
free(p);
p = NULL;
}
}
void printList(linkedList_h* L)
{
listNode* p;
printf("L = (");
p = L->head;
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("%s", p->data);
p = p->link;
if (p != NULL) printf(", ");
}
printf(") \n");
}
listNode* createNode(char* x)
{
listNode* newNode;
newNode = (listNode*)malloc(sizeof(listNode));
strcpy(newNode->data, x);
newNode->link = NULL;
return newNode;
}
void insertFirstNode(linkedList_h* L, char* x)//i()."수"
{
listNode* newNode;
newNode = createNode(x);
newNode->link = L->head;
L->head = newNode;
}
void insertMiddleNode(linkedList_h* L, listNode* pre, char* x)
{
listNode* newNode;
newNode = createNode(x);
if (L->head == NULL)
{
L->head = newNode;
}
else if (pre == NULL)
{
L->head = newNode;
}
else
{
newNode->link = pre->link;
pre->link = newNode;
}
}
void insertLastNode(linkedList_h* L, char* x)
{
listNode* newNode;
listNode* p;
newNode = createNode(x);
if (L->head == NULL)
{
L->head = newNode;
return;
}
p = L->head;
while (p->link != NULL)
p = p->link;
p->link = newNode;
}
int main() {
linkedList_h* L;
L = createLinkedList_h();
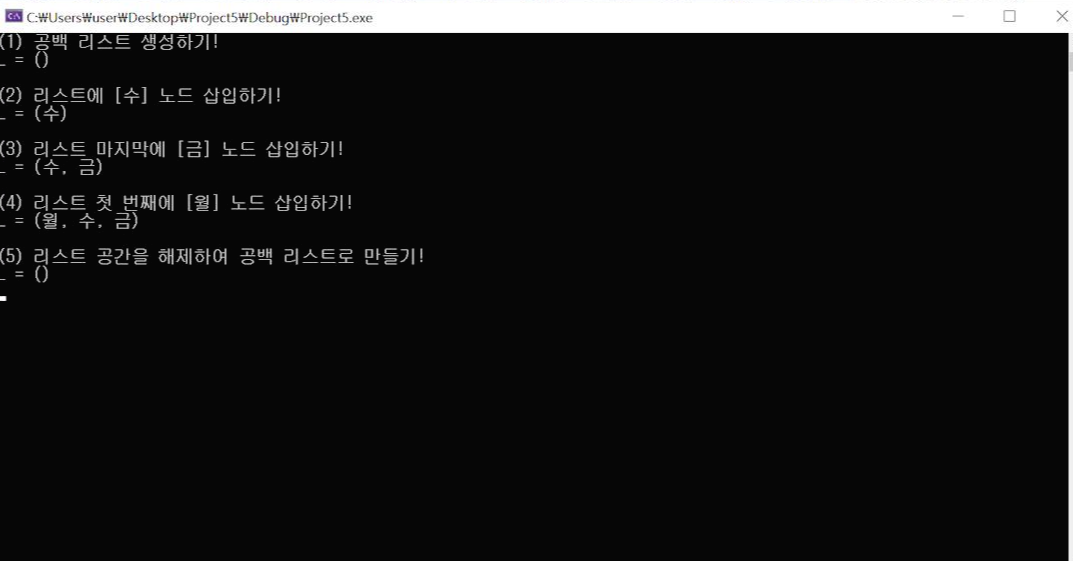
printf("(1) 공백 리스트 생성하기! \n");
printList(L); getchar();
printf("(2) 리스트에 [수] 노드 삽입하기! \n");
insertMiddleNode(L, NULL, "수");
printList(L); getchar();
printf("(3) 리스트 마지막에 [금] 노드 삽입하기! \n");
insertMiddleNode(L,L->head, "금");
printList(L); getchar();
printf("(4) 리스트 중간에 [목] 노드 삽입하기! \n");
insertMiddleNode(L, L->head, "목");
printList(L); getchar();
printf("(5) 리스트 공간을 해제하여 공백 리스트로 만들기! \n");
freeLinkedList_h(L);
printList(L);
getchar();
return 0;
}
실행 결과2
Source Code3
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// 단순 연결 리스트의 노드 구조를 구조체로 정의
typedef struct ListNode
{
char data[4];
struct ListNode* link;
} listNode;
// 리스트의 시작을 나타내는 head 노드를 구조체로 정의
typedef struct
{
listNode* head;
} linkedList_h;
// 공백 연결 리스트를 생성하는 연산
linkedList_h* createLinkedList_h(void)
{
linkedList_h* L;
L = (linkedList_h*)malloc(sizeof(linkedList_h));
L->head = NULL; // 공백 리스트이므로 NULL로 설정
return L;
}
// 연결 리스트의 전체 메모리를 해제하는 연산
void freeLinkedList_h(linkedList_h* L)
{
listNode* p;
while (L->head != NULL)
{
p = L->head;
L->head = L->head->link;
free(p);
p = NULL;
}
}
// 연결 리스트를 순서대로 출력하는 연산
void printList(linkedList_h* L)
{
listNode* p; //루프변수
printf("L = (");
p = L->head;
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("%s", p->data);
p = p->link;
if (p != NULL) printf(", ");
}
printf(") \n");
}
listNode* createNode(char* x)
{
listNode* newNode;
newNode = (listNode*)malloc(sizeof(listNode)); // 삽입할 새 노드 할당
strcpy(newNode->data, x); // 새 노드의 데이터 필드에 x 저장
newNode->link = NULL;
return newNode; //주소를 반환
}
// 첫 번째 노드로 삽입하는 연산
void insertFirstNode(linkedList_h* L, char* x)
{
listNode* newNode;
newNode = createNode(x);
newNode->link = L->head;
L->head = newNode;
}
// 노드를 pre 뒤에 삽입하는 연산
void insertMiddleNode(linkedList_h* L, listNode* pre, char* x)
{
listNode* newNode;
newNode = createNode(x);
if (L == NULL)
{ // 공백 리스트인 경우
newNode->link = NULL; // 새 노드를 첫 번째이자 마지막 노드로 연결
L->head = newNode;
}
else if (pre == NULL)
{ // 삽입 위치를 지정하는 포인터 pre가 NULL인 경우
L->head = newNode; // 새 노드를 첫 번째 노드로 삽입
}
else
{
newNode->link = pre->link; // 포인터 pre의 노드 뒤에 새 노드 연결
pre->link = newNode;
}
}
// 마지막 노드로 삽입하는 연산
void insertLastNode(linkedList_h* L, char* x)
{
listNode* newNode;
listNode* p;
newNode = createNode(x);
if (L->head == NULL)
{ // 현재 리스트가 공백인 경우
L->head = newNode; // 새 노드를 리스트의 시작 노드로 연결
return;
}
// 현재 리스트가 공백이 아닌 경우
p = L->head;
while (p->link != NULL)
p = p->link; // 현재 리스트의 마지막 노드를 찾음
p->link = newNode; // 새 노드를 마지막 노드(temp)의 다음 노드로 연결
}
int main()
{
linkedList_h* L;
L = createLinkedList_h();
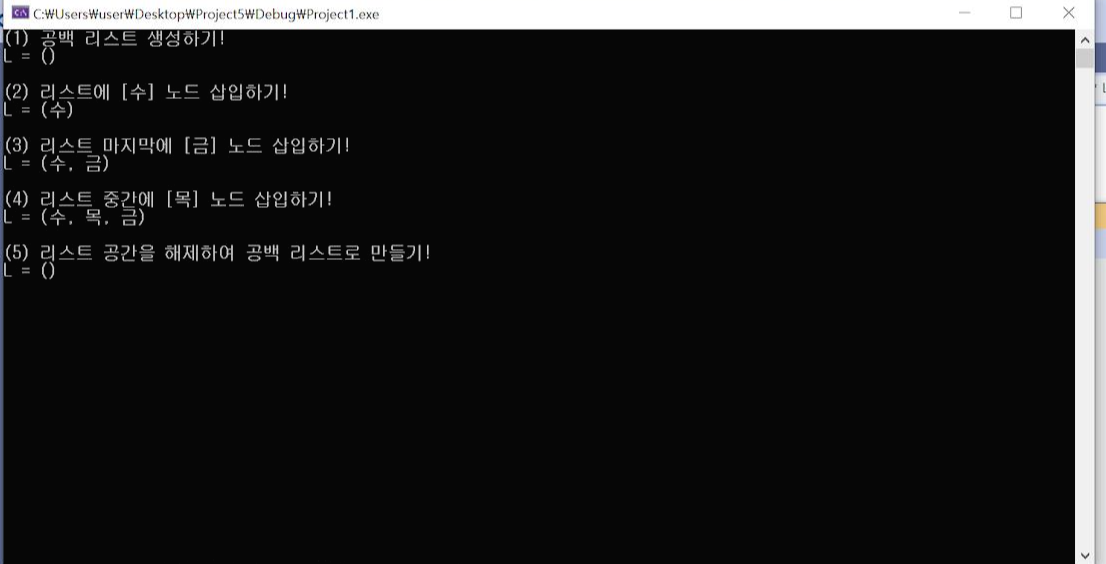
printf("(1) 공백 리스트 생성하기! \n");
printList(L); getchar();
printf("(2) 리스트에 [목] 노드 삽입하기! \n");
insertFirstNode(L, "목");
printList(L); getchar();
printf("(3) 리스트 첫번째에 [월] 노드 삽입하기! \n");
insertFirstNode(L, "월");
printList(L); getchar();
printf("(4) 리스트 마지막에 [금] 노드 삽입하기! \n");
insertLastNode(L,"금");
printList(L); getchar();
printf("(5) 리스트 공간을 해제하여 공백 리스트로 만들기! \n");
freeLinkedList_h(L);
printList(L);
getchar();
return 0;
}
실행 결과3
Source Code4
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// 단순 연결 리스트의 노드 구조를 구조체로 정의
typedef struct ListNode
{
char data[4];
struct ListNode* link;
} listNode;
// 리스트의 시작을 나타내는 head 노드를 구조체로 정의
typedef struct
{
listNode* head;
} linkedList_h;
// 공백 연결 리스트를 생성하는 연산
linkedList_h* createLinkedList_h(void)
{
linkedList_h* L;
L = (linkedList_h*)malloc(sizeof(linkedList_h));
L->head = NULL; // 공백 리스트이므로 NULL로 설정
return L;
}
// 연결 리스트의 전체 메모리를 해제하는 연산
void freeLinkedList_h(linkedList_h* L)
{
listNode* p;
while (L->head != NULL)
{
p = L->head;
L->head = L->head->link;
free(p);
p = NULL;
}
}
// 연결 리스트를 순서대로 출력하는 연산
void printList(linkedList_h* L)
{
listNode* p; //루프변수
printf("L = (");
p = L->head;
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("%s", p->data);
p = p->link;
if (p != NULL) printf(", ");
}
printf(") \n");
}
listNode* createNode(char* x)
{
listNode* newNode;
newNode = (listNode*)malloc(sizeof(listNode)); // 삽입할 새 노드 할당
strcpy(newNode->data, x); // 새 노드의 데이터 필드에 x 저장
newNode->link = NULL;
return newNode; //주소를 반환
}
// 첫 번째 노드로 삽입하는 연산
void insertFirstNode(linkedList_h* L, char* x)
{
listNode* newNode;
newNode = createNode(x);
newNode->link = L->head;
L->head = newNode;
}
// 노드를 pre 뒤에 삽입하는 연산
void insertMiddleNode(linkedList_h* L, listNode* pre, char* x)
{
listNode* newNode;
newNode = createNode(x);
if (L == NULL)
{ // 공백 리스트인 경우
newNode->link = NULL; // 새 노드를 첫 번째이자 마지막 노드로 연결
L->head = newNode;
}
else if (pre == NULL)
{ // 삽입 위치를 지정하는 포인터 pre가 NULL인 경우
L->head = newNode; // 새 노드를 첫 번째 노드로 삽입
}
else
{
newNode->link = pre->link; // 포인터 pre의 노드 뒤에 새 노드 연결
pre->link = newNode;
}
}
// 마지막 노드로 삽입하는 연산
void insertLastNode(linkedList_h* L, char* x)
{
listNode* newNode;
listNode* p;
newNode = createNode(x);
if (L->head == NULL)
{ // 현재 리스트가 공백인 경우
L->head = newNode; // 새 노드를 리스트의 시작 노드로 연결
return;
}
// 현재 리스트가 공백이 아닌 경우
p = L->head;
while (p->link != NULL)
p = p->link; // 현재 리스트의 마지막 노드를 찾음
p->link = newNode; // 새 노드를 마지막 노드(temp)의 다음 노드로 연결
}
int main()
{
linkedList_h* L;
L = createLinkedList_h();
printf("(1) 공백 리스트 생성하기! \n");
printList(L); getchar();
printf("(2) 리스트에 [수] 노드 삽입하기! \n");
insertMiddleNode(L, NULL, "수");
printList(L); getchar();
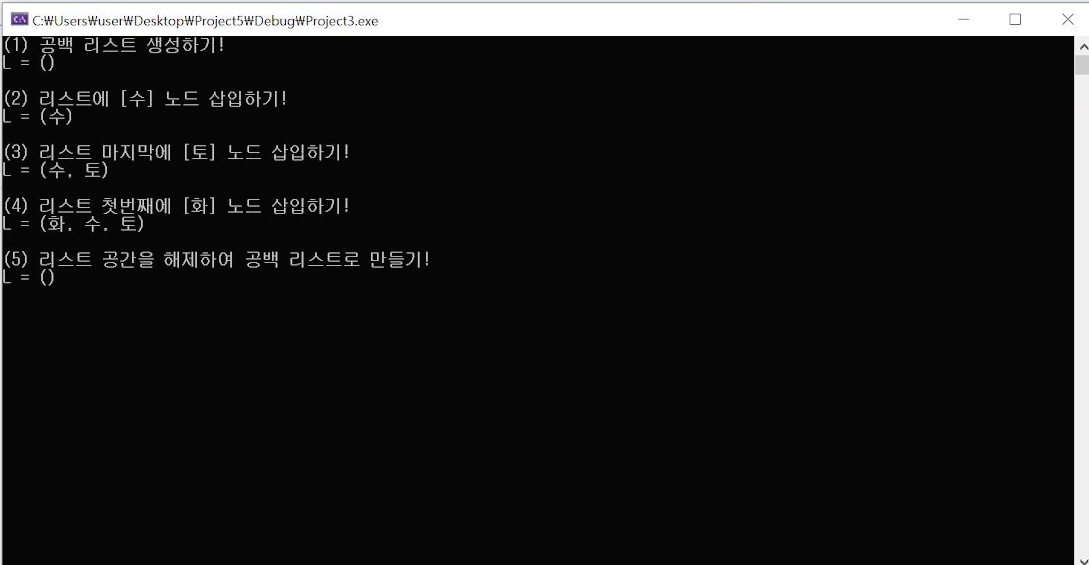
printf("(3) 리스트 마지막에 [토] 노드 삽입하기! \n");
insertLastNode(L, "토");
printList(L); getchar();
printf("(4) 리스트 첫번째에 [화] 노드 삽입하기! \n");
insertFirstNode(L, "화");
printList(L); getchar();
printf("(5) 리스트 공간을 해제하여 공백 리스트로 만들기! \n");
freeLinkedList_h(L);
printList(L);
getchar();
return 0;
}
실행 결과